Water Resources: the Blue Capital
-- a note from _kt75
In continuation of the recent article on prospective water prices [1] this article provides a brief and overall impression of how sustainable water management might be affected by environmental, technical, economic and geo-political conditions in the future.
In continuation of the recent article on prospective water prices [1] this article provides a brief and overall impression of how sustainable water management might be affected by environmental, technical, economic and geo-political conditions in the future.
In principle, water shouldn't be considered as an commercial entity (subject to speculation) rather as a global and (preferably) commonly available good. The reality however, looks different: increasingly, but not yet recognized by the broad public, water has become a strong, almost unique issue. It is already today the 'blue gold' with a rather limited access [2]-[5]. The latter aspect will accentuate in the future and the situations to come can be formulated as follows:
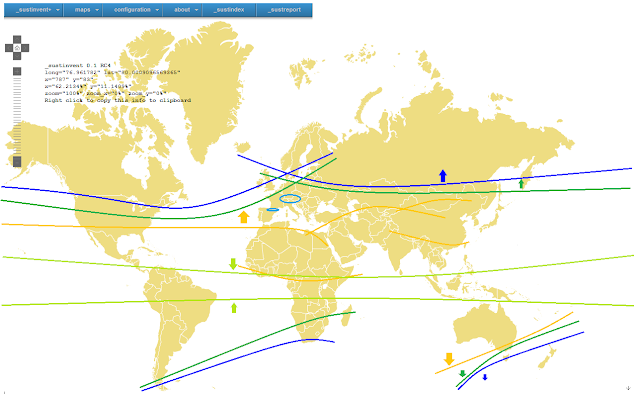
Key water resources for humans are water reservoirs, either surface (rivers, lakes, ponds, etc.) or sub-surface (aquifers). Due to worsening environmental, economic, etc. conditions it is expected that regions with stable water conditions (blue line regions) will experience a shift towards the North (Northern hemisphere) and the South (Southern hemisphere) respectively, whereby overall the water conditions in the Northern Hemisphere are qualitatively better than in the Southern hemisphere. The blue line regions posses rather stable water reservoirs surface and sub-surface. In addition, their water reservoirs are characterised by healthy replenishment rates. Undercapacities do not exist.
As the blue line regions the green line regions will experience a shift towards North (and to the South in the Southern hemisphere adequately). The water conditions of the green line regions are still balanced but require careful management. Key water resources are rather of surface kind (rivers, lakes, etc.) and a notable meteorological influence exists. For example can dry summers seriously affect the surface water reservoirs of the green line regions. Results might be: shortages in drinking water, failures in waste water treatment facilities/canalisation, impacts on industry, etc. To address this issue various stakeholders have started undertakings to address these unavoidable future conditions [6], [7]. The green line regions experience a notable pressure from the adjacent orange line regions. These regions suffer from serious water problems. Water is only temporarily available and the quality is fluctuating. Key water resources are lakes and rivers, which periodically fall dry. Groundwater is rather rare and if available it has often a dramatically low replenishment rate (e.g. Disi-Aquifer [8]). Currently neither Europe nor the US, for example, have such conditions but due to the global warming it is to be expected that environmentally risky orange line conditions will spread further towards the North. In Europe in particular Portugal, Spain, Italy and Southern part of France are vulnerable to dropping water reservoirs, which is also a result of the ongoing economic and social distortions. In the further future and despite the water 'generator' the Alps also countries like Switzerland, Austria and Germany may face serious water shortage problems. The reason is that mountains on a large scale represent only a 'water container'. In case of e.g. missing rainfall the supply with fresh water will be interrupted. Accordingly, preparative measures to preserve stable water conditions are recommendable.
A special case represent the tropical regions. Despite (from a meteorological perspective) a stable and continuous water supply these regions suffer from unstable water conditions. Prime reasons might be missing investments, inappropriate technical facilities and missing process know-how.
References: [1], [2], [3], [4], [5], [6], [7], [8]
---
Prominent _kt75 Publications:
► An inconvenient truth: the green business bubble bursts in... (click here to participate) - More than 170 participants voted on the teaser poll: How about you?